





Published on Apr 02, 2024
A tire or tyre is a device covering the circumference of a wheel. It is an essential part of most ground vehicles and is used to dampen the oscillations caused by irregularities in the road surface, to protect the wheel from wear and tear as well as to provide a high-friction bond between the vehicle and the ground to improve acceleration and handling.
In most vehicles, either the front or rear tires will wear faster than the others. Having mismatched tread depths can alter the handling of the car in unacceptable ways - so it is generally advisable to swap the front and rear tires as they wear down to even out the wear patterns. This is called rotating the tires. If the vehicle's suspension is somewhat out of adjustment, it is also possible for the tires to wear more on one side than the other - so it may also be beneficial to rotate the tires from one side of the car to the other - however, careful attention should be paid to the owner's manual since some vehicles require particular tire rotation patterns.
Notably, some tires are designed to provide best traction only when spinning in a clockwise or counter-clockwise direction. In such cases one must not rotate the tires from one side of the car to the other because that would put a 'clockwise tire' onto a wheel that turns in a counter-clockwise direction. Such tires typically have an arrow moulded into the sidewall to indicate the preferred direction.
Performance tires tend to be designed for use at higher speeds. They often have a softer rubber compound for improved traction, especially on high speed cornering. The trade off of this softer rubber is a lower treadwear rating.
Winter tires are designed to provide improved performance under winter conditions compared to tires made for use in summer. The rubber compound used in the tread of the tire is usually softer than that used in tires for summer conditions, so providing better grip on ice and snow. Winter tires often have fine grooves and siping in the tread patterns that are designed to grip any unevenness on ice. Winter tires are usually removed for storage in the spring, because the rubber compound becomes too soft in warm weather resulting in a reduced tire life.
These are an attempt to make a tire that will be a compromise between a tire developed for use on dry and wet roads during summer, and a tire developed for use under winter conditions, when there is snow and ice on the road. However, the type of rubber and the tread pattern best suited for use under summer conditions cannot, for technical reasons, give good performance on snow and ice. The all-season tire is therefore a poor compromise, and is neither a good summer tire, nor a good winter tire.
All-terrain tires are typically used on SUVs and light trucks. These tires often have stiffer sidewalls for greater resistance against puncture when traveling off-road, the tread pattern offers wider spacing than all-season tires to evacuate mud from the tread.
Mud terrain tires are characterized by large, chunky tread patterns designed to bite into muddy surfaces and provide grip. The large open design also allows mud to clear more quickly from between the lugs.
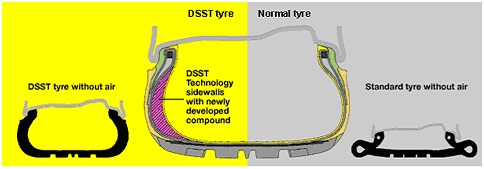
The diagram below shows the Dunlop DSST run flat system. These tyres can be placed on any rim - the sidewall is reinforced allowing the tyre to support the vehicle's weight. The tyre is constructed with new rubber compounds that prevent tyre destruction with excessive flexing.Run Flat Tyres allow a vehicle with complete loss of tyre pressure to handle effectively. Braking, acceleration, and steering behaviour remain unchanged. Mobility is also maintained even after a puncture, but you must refer to each individual tyre’s guidelines from the Manufacturer.
Tyres that carry this technology include the Bridgestone RFT series, Continental SSR series Dunlop DSST series,Goodyear ROF series, and the Pirelli Euphori@ series.
The rubber clip prevents the tyre rim cutting into your tyre when you experience a sudden loss of pressure. This system has been developed byMichelin and is known as the PAX System. Like the reinforced sidewall it operates in tandem with automated tyre pressure monitors.
Why would you want to do this? The benefits of Nitrogen filling are as follows:
• Improved comfort of ride
• Improved safety
• Increased fuel savings
• Improved life of tyre
Nitrogen has long been the accepted gas medium for filling aircraft tyres, racing tyres and heavy mining and construction vehicle tyres. Nitrogen is used for safety reasons and to ensure that tyres are always at a constant pressure. Compressed air, the traditional medium for inflating car tyres, contains both oxygen (21%) and nitrogen (78%).
The rubber tyre is like a membrane, through which oxygen permeates three times faster than the nitrogen. The result is that the oxygen slowly leaks out through the rubber walls, and the under-inflation leads to higher tyre wear with a consequent decrease in safety and comfort, and higher fuel costs.
| Are you interested in this topic.Then mail to us immediately to get the full report.
email :- contactv2@gmail.com |